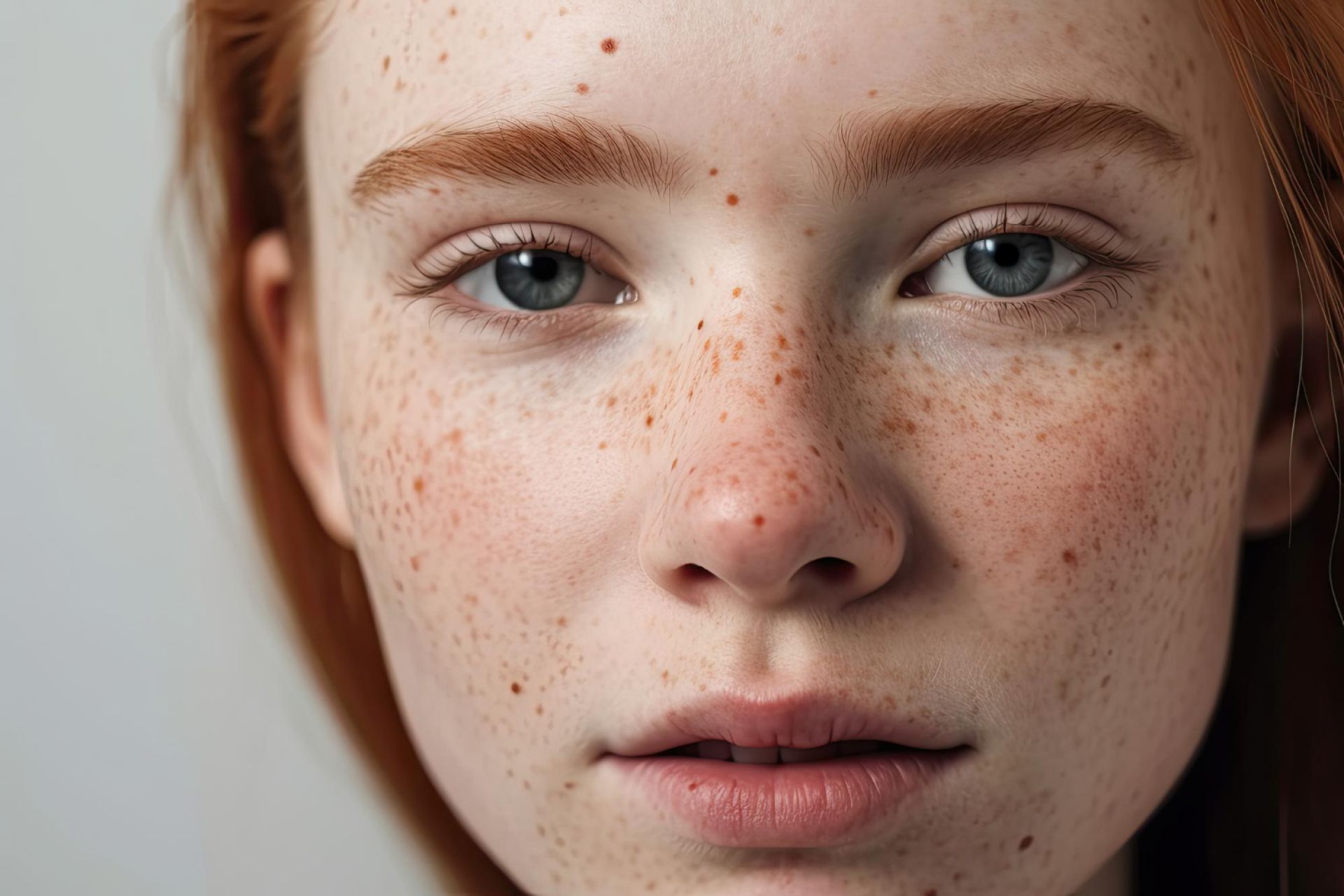
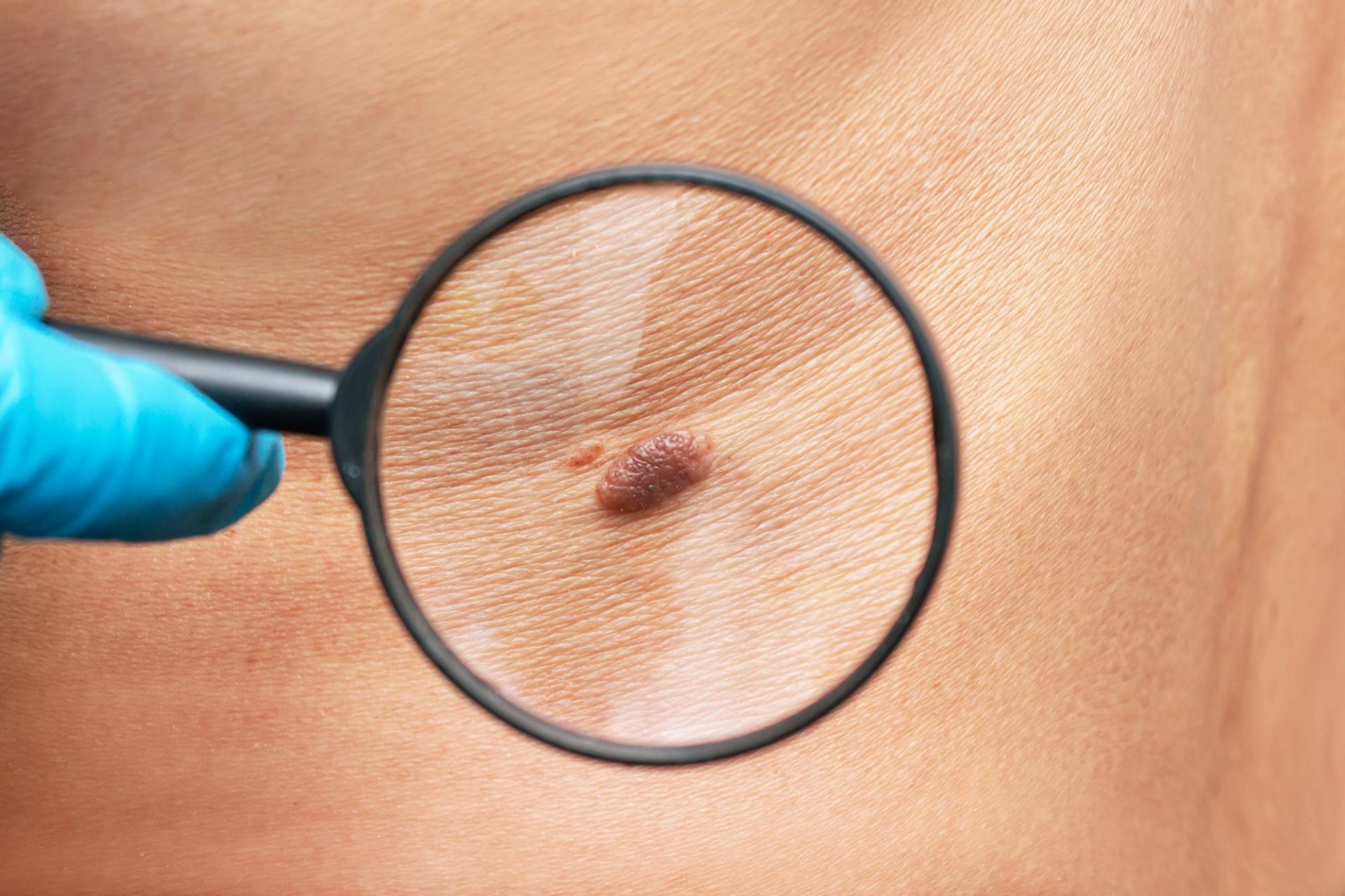
A mole usually looks like a small spot on the skin. Moles are also known as nevi or beauty marks. These are common and mostly harmless. They are not contagious and should not hurt, itch or bleed.
You can schedule a consultation with a dermatologist if you suspect you have an abnormal mole or are concerned about the appearance of moles. Dermatologists on the Digital Clinics platform have proven experience in evaluating, diagnosing and treating dermatological conditions.
What a normal mole looks like
The skin is the largest organ of the body. Skin moles (nevus is the medical terms) are skin growths that range in color from natural skin tone to brown or black. Moles can appear anywhere on the skin or mucous membranes, alone or in groups.
Most moles appear in early childhood or in the first 20 years of life. It is therefore normal for a person to have between 10 and 40 moles by adulthood.
The life cycle of a mole is about 50 years. As the years go by, moles usually change slowly, becoming raised and lighter in color. Sometimes hairs grow through moles. Some moles do not change at all, while others slowly disappear over time.
What are the types of moles?
Common nevi
These are normal moles - small growths on the skin, pink, beige or brown, with clear edges.
Congenital nevi
These are what we call birthmarks. Congenital nevi occur in about one in 100 people. These nevi may be more likely to develop into melanoma than nevi that appear after birth. If your nevus is larger than eight millimetres in diameter, it has a higher risk of becoming cancerous.
Dysplastic nevi
These nevi are larger than a pencil eraser and have an irregular shape. Dysplastic nevi tend to be uneven in color, with a dark brown center and lighter, uneven edges. These nevi are usually inherited, and people who have them can have more than 100 nevi. If you have dysplastic nevi, you have a higher chance of developing malignant melanoma (skin cancer). Any change in a nevus should be checked by a dermatologist. Or, even better is to schedule annually moles screening.
Symptoms and causes
What causes moles to appear?
Moles occur when skin cells, called melanocytes, grow abnormally in clusters instead of all over the surface of the skin.
What are the risk factors for cancerous moles?
The most important risk factor is uncontrolled sun exposure.
What makes moles darker?
Moles can darken after sun exposure, during pregnancy, and during puberty. During pregnancy, moles often change evenly due to hormonal effects. For example, they may darken or become larger. However, if a mole changes in an irregular or uneven manner, it should be evaluated by a dermatologist.
Diagnosis and analysis
Why should I do the mole self-examination?
The skin is the largest organ of the body, and it's also in plain sight, which gives you the opportunity to keep an eye on it easily and be proactive in preventing skin cancer.
You are more likely to get skin cancer if you:
- You have lighter skin
- You have many moles on your body
- Close family members have many moles, atypical moles, or a history of skin cancer
In addition to limiting exposure to sunlight and using sunscreen every day, examining moles increases the chances of detecting and treating melanoma and other skin cancers early.
Dermatologists recommend examining your skin every month. Most moles are benign (non-cancerous). If you notice changes in the color or appearance of a mole, make an appointment with a dermatologist. You should also check moles if they bleed, sting, itch, look scaly, or become tender or painful.
What to look for when examining moles
Most moles are benign (non-cancerous). Moles of medical concern are those that look different or appear on the skin after the age of 30. If you notice changes in color, thickness, size, or shape, you should see a dermatologist. You should also check your moles if they bleed, ooze, itch, peel, become tender or painful.
Where you don't have access, such as on your back, use a mirror or ask someone to help you. Pay special attention to areas of the skin that are often exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, legs (especially in women), arms, chest and back (especially in men).
If a mole shows any of the signs listed below, get the mole checked out by a dermatologist right away:
- Asymmetry: If one half of your skin mole doesn't match the other half
- Border: If the edges or borders of the mole are ragged, blurred, or irregular
- Color: If the color of the mole is not the same everywhere or has shades of several colors, such as tan, brown, black, blue, white or red
- Diameter: If the diameter of the mole is larger than a pencil eraser
- Elevation/Evolution: If the mole becomes elevated or changes over a short period of time
-
The most common location of melanoma in men is the back; in women, it is the lower leg.
Melanoma is the most common cancer in women aged 25 to 29.
What does the dermatologist do if you have a suspicious mole?
Normal (benign) moles do not need to be removed. However, if the dermatologist determines that the mole is abnormal, he will perform a skin biopsy, in which a small sample is taken from the mole to be examined under a microscope. A diagnosis can usually be made based on biopsy results. If the mole is found to be cancerous, it must be removed completely.
Treatment of suspicious moles
What doctor treats moles?
Your family doctor may refer you to a skin health specialist (a dermatologist).
Do moles need to be removed?
A normal mole does not need to be removed. If you still decide to do it, keep in mind that you may be left with a scar.
How are moles removed?
Never try to remove a mole at home, even if you use professional medical products. It is very important that the extirpation of moles is done by a medical professional, in a specially dedicated space, in order not to get an infection and to analyse in advance whether the mole is cancerous or not.
Prevention
Can moles be prevented?
Moles are natural skin growths that cannot be prevented. However, what can be prevented is skin cancer. Or, if not prevented, at least discovered in the early stages, which significantly increases the success rate against the disease.
How to prevent skin cancer
- Stay in the sun as little as possible
- Wear sunscreen every day (UV creams or clothing)
- Examine your moles monthly, looking for specific signs
Being proactive about skin cancer is very important to your health, especially if you:
- You have fair skin
- You have many moles on your skin
- Other family members have had skin cancer or have many moles on their skin
If you need advice or an expert opinion on this topic, on the Digital Clinics platform you can upload several photos of the moles that concern you, and an experienced dermatologist can assess your situation online and give you the answers you need.